last modified: 2023-05-15

|
Not a closed list, not a recipe! Rather, these are essential building blocks for a strategy of value creation based on data. |
1. Predict

a. Examples of companies
-
Predicting crime

-
Predicting deals

-
Predictive maintenance

b. Obstacles and difficulties
-
Risk missing the long tail, algorithmic discrimination, stereotyping
-
Neglect of novelty
2. Suggest

a. Examples of companies
-
Amazon’s product recommendation system

-
Google’s “Related searches…”

-
Retailer’s personalized recommendations

b. Obstacles and difficulties
-
The cold start problem, managing serendipity and filter bubble effects.
-
Finding the value proposition which goes beyond the simple “you purchased this, you’ll like that”
3. Curate

a. Examples of companies
-
Clarivate Analytics curating metadata(data, data curation) from scientific publishing

-
Nielsen and IRI curating and selling retail data


-
ImDB curating and selling movie data

-
NomadList providing practical info on global cities for nomad workers

b. Obstacles and difficulties
-
Slow progress: curation needs human labor to insure high accuracy, it does not scale the way a computerized process would.
-
Must maintain continuity: missing a single year or month hurts the value of the overall dataset.
-
Scaling up / right incentives for the workforce: the workforce doing the digital labor of curation should be paid fairly, which is not the case yet.
-
Quality control
4. Enrich

Examples of companies
-
Selling methods and tools to enrich datasets

-
Selling aggregated indicators

-
Selling credit scores
Obstacles and difficulties
-
Knowing which cocktail of data is valued by the market
-
Limit duplicability
-
Establish legitimacy
5. Rank / match / compare

Examples of companies
-
Search engines ranking results

-
Yelp, Tripadvisor, etc… which rank places

-
Any system that needs to filter out best quality entities among a crowd of candidates
Obstacles and difficulties
-
Finding emergent, implicit attributes (imagine: if you rank things based on just one public feature: not interesting nor valuable)
-
Insuring consistency of the ranking (many rankings are less straightforward than they appear)
-
Avoid gaming of the system by the users (for instance, companies try to play Google’s ranking of search results at their advantage)
6. Segment / classify

Examples of companies
-
Tools for discovery / exploratory analysis by segmentation
-
Diagnostic tools (spam or not? buy, hold or sell? healthy or not?)

Obstacles and difficulties
-
Evaluating the quality of the comparison
-
Dealing with boundary cases
-
Choosing between a pre-determined number of segments (like in the k-means) or letting the number of segments emerge
7. Generate / synthesize

Examples of companies
-
OpenAI with ChatGPT
Obstacles and difficulties
-
Legal framework still being shaped (what about the copyright of the content ChatxGPT has been trained on?)
-
Still new, no "textbook" on how to use it at its fullest potential
Combos
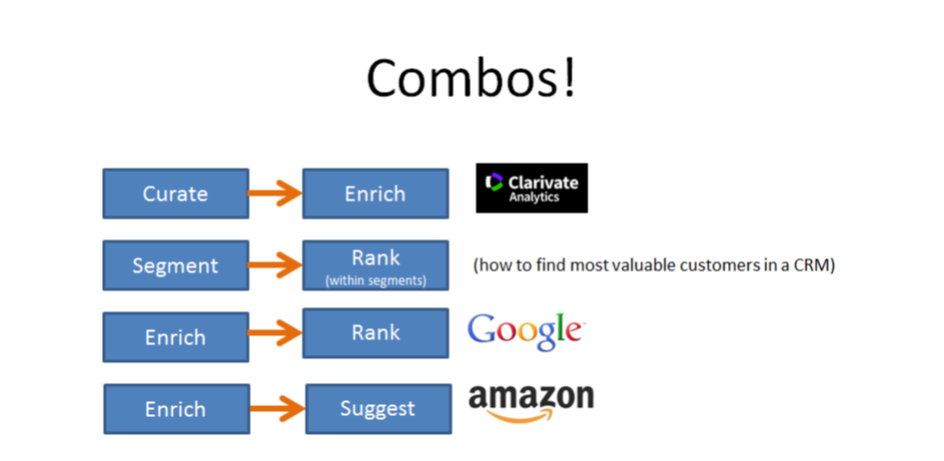
The end
Find references for this lesson, and other lessons, here.

This course is made by Clement Levallois.
Discover my other courses in data / tech for business: https://www.clementlevallois.net
Or get in touch via Twitter: @seinecle